The construction industry, known for its traditional methods and processes, is experiencing a paradigm shift with the advent of 3D printing technology. Often hailed as a revolutionary approach to construction, 3D printing has garnered attention for its potential to transform how buildings and structures are designed and built. This article delves into the rise of 3D printing in construction, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and the ongoing debate surrounding its status as a revolutionary innovation or mere hype.
The Basics of 3D Printing in Construction:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves the layer-by-layer deposition of materials to create three-dimensional objects. In construction, this technology utilizes concrete or other suitable building materials to fabricate entire structures or components layer by layer, following a digital design.
Applications of 3D Printing in Construction:
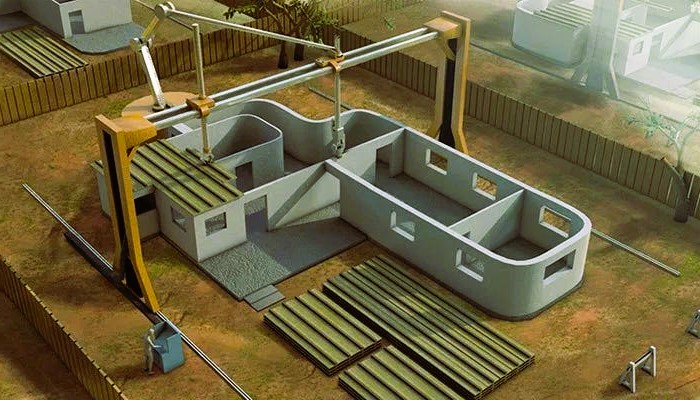
- Building Components:3D printing is commonly used to fabricate building components such as walls, columns, and beams. The layering process allows for intricate designs and complex geometries that may be challenging or costly to achieve using traditional construction methods.
- Customization:The flexibility of 3D printing enables the customization of building elements based on specific project requirements. Architects and designers can create unique and innovative designs that cater to both aesthetic and functional considerations.
- Affordable Housing:One of the touted benefits of 3D printing in construction is its potential to address affordable housing challenges. By automating the construction process, 3D printing has the potential to reduce labor costs and expedite project timelines, making housing more accessible.
- Rapid Prototyping:3D printing allows for the rapid prototyping of architectural designs. This iterative process enables architects and builders to visualize and test concepts quickly, facilitating more informed decision-making in the design phase.
- Complex Architectural Forms:Traditional construction methods often struggle with the realization of complex architectural forms. 3D printing, on the other hand, excels in creating intricate and unconventional shapes, pushing the boundaries of architectural design. Did you like the article? We recommend that you read Deep Dive into Concrete.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Construction:
- Speed and Efficiency:3D printing can significantly expedite the construction process. The layer-by-layer additive manufacturing technique eliminates the need for multiple steps in traditional construction, resulting in faster project delivery.
- Reduced Material Waste:Traditional construction often generates considerable material waste. 3D printing is a more sustainable option as it produces minimal waste by using only the required amount of material for the project.
- Cost Savings:The potential for cost savings in 3D printing lies in reduced labor costs and optimized material usage. The automation of construction tasks and the ability to print on-site contribute to overall cost-effectiveness.
- Design Freedom:3D printing provides unparalleled design freedom. Architects can experiment with intricate and unconventional designs that may be challenging or impossible to achieve using traditional construction methods.
- Accessibility:The affordability associated with 3D printing has the potential to make housing more accessible, particularly in regions facing housing shortages or in need of rapid construction solutions.
Challenges and Skepticism:
- Scale and Size Limitations:While 3D printing has proven effective for smaller structures and components, scaling up to larger buildings presents challenges. The technology is still evolving to address the construction of sizable structures with the same efficiency.
- Material Considerations:The materials used in 3D printing must meet stringent structural and durability requirements. Developing suitable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly construction materials for 3D printing remains an ongoing challenge.
- Regulatory and Standardization Challenges:The construction industry is highly regulated, and incorporating 3D printing into mainstream construction practices requires adherence to existing regulations and the development of new standards. The lack of standardized processes poses challenges to widespread adoption.
- Technological Limitations:Current 3D printing technology may struggle with certain architectural features, and its effectiveness can be influenced by factors such as weather conditions. Advancements are needed to overcome these limitations and ensure reliability.
- Integration with Existing Construction Practices:Integrating 3D printing with existing construction practices and supply chains is a complex task. Compatibility with traditional construction methods and materials is crucial for seamless collaboration on construction sites.
Revolutionary or Hype: The Ongoing Debate:
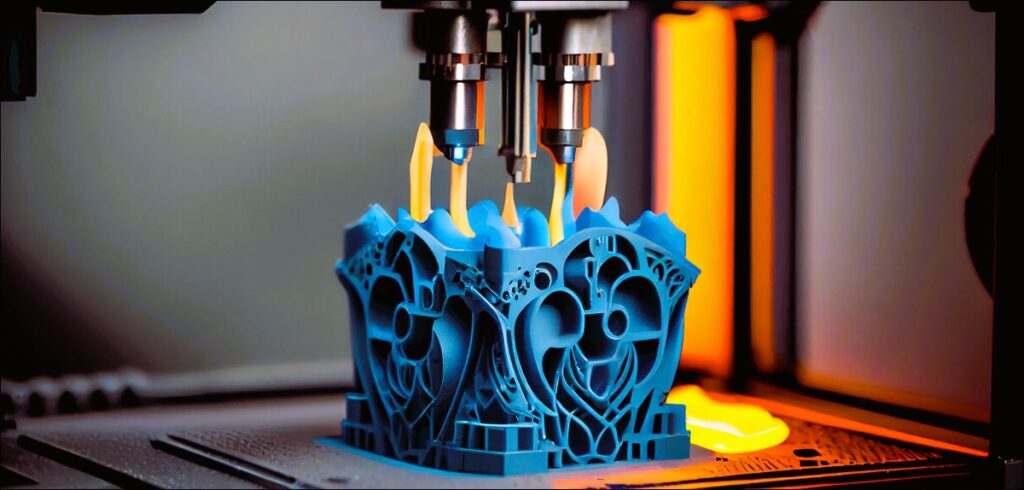

The rise of 3D printing in construction has sparked a heated debate within the industry and among experts. Proponents argue that 3D printing is a revolutionary force that will redefine the way we build, offering unparalleled efficiency, affordability, and design freedom. They envision a future where 3D printing becomes the standard for construction projects of all sizes.
On the other hand, skeptics question the scalability and practicality of 3D printing in construction. They argue that, while 3D printing has demonstrated success in certain applications, its widespread adoption for large-scale projects faces significant hurdles. The challenges related to material properties, regulatory frameworks, and integration with existing practices cast doubt on the transformative potential of 3D printing.
Industry Standards and Guidelines:
To address the challenges and ensure the responsible adoption of 3D printing in construction, industry standards and guidelines play a crucial role. Establishing standardized processes, material specifications, and regulatory frameworks is essential for building confidence in the technology and fostering its integration into mainstream construction practices.
For in-depth information on 3D printing in construction and industry standards, readers are encouraged to explore resources provided by Wikipedia. These platforms offer valuable insights into the current state of 3D printing technology, ongoing research, and the evolving landscape of construction practices.
Conclusion:
The rise of 3D printing in construction undoubtedly brings innovation and potential to the industry. Whether it will be truly revolutionary or deemed as hype depends on the industry’s ability to address current challenges, embrace technological advancements, and establish robust standards and guidelines. While 3D printing has already proven its efficacy in certain applications, the journey to widespread adoption requires a collaborative effort from architects, builders, regulators, and technology developers. As the technology evolves and industry practices adapt, the transformative impact of 3D printing in construction may yet redefine the way we conceive, design, and construct the built environment.